In recent years, the diagnosis of medical image becomes more complicated with the existing systems. The classical image segmentation method uses the relevant data with particular texture, size and connectivity between the pixels for better performance of less noise images. The diagnosis of cardiovascular involved in complex procedures whereas the analysis of blood vessels carried out. The image segmentation technique is used to eliminate such complexities in Ultrasound carotid image diagnosis. The common carotid artery image is extracted from ultrasound scanner and the steps given in the flow diagram have been followed:
Fig.1 Flow diagram for the segmentation algorithm
A. Image Acquisition
In image acquisition ultrasound scanner is used to acquire the data to record the motion of the arterial wall and video recorder assists in recording the movements.
B. Histogram Equalization
The Histogram Equalization method has been used to improve the appearance of the CCA image by adjusting intensity values without an error in the structure of intima media layer.
C. Detection of Interested Region
The Interested region defines the position of Intima Media layer in the castigate area of ultrasound image. The region presented at the surroundings of the interface has been considered as a region of interest which distinguishes the blood and tissue of carotid arteries
D. Gaussian Filtering
The image obtained from the previous step has been prefiltered earlier to threshold technique. gaussian filtering is used to attenuate speckle noise which presents in the ultrasound image without disturbing any important features of the image.
E. Threshold Technique
The thresholding algorithm is enforced to discover the interface of two main image classes such as lumen and carotid artery tissues. The pixels are partitioned depending on their intensity value. It results in values 0 and 255.
f(x,y) = 255 if f(x,y) > T (1)
0 if f(x,y) ≤ T
where f(x,y) denotes the intensity value of input image at the location of (x,y) and the value of T varying from 85 to 120 which extracts the lumen-intima interface.
F. Dilation
Dilation of image is a basic operation of mathematical morphology. It uses a horizontal structure element for examining and flourishing the intimal layer contained in the threshold image to provide continuity between the pixels of lumen-intima interface.
G. Auto-Median Filtering
The median filter used to remove noise present in dilated carotid artery image. This noise reduction is a typical post-processing step to improve the results of threshold image.
H. Implementation in Virtex FPGA kit
The Virtex series of FPGA is desirable for implementing the image processing algorithm. The hardware implementation provides the advantage of the high parallelism in the algorithm.
Result:
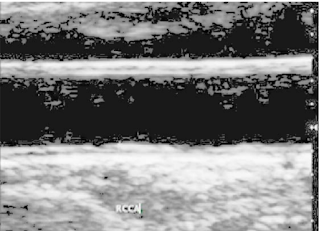
The CCA image is extracted from
ultrasound scanner and the steps given in the flow diagram
have been followed. The single frame has been acquired and
used for further analysis. The longitudinal section acquired
input image as shown in Fig.2a. & Fig.2b shows the Preprocessed image, it is used to enhance the contrast of input
image.
Fig.2a
Fig.2bReferences:
R. Hemalatha, N. Santhiyakumari and S. Suresh, "Implementation of medical image segmentation using Virtex FPGA kit," 2015 International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Engineering Systems, Guntur, India, 2015, pp. 358-362, doi: 10.1109/SPACES.2015.7058283.


Comments
Post a Comment